IoT in Healthcare Use Cases eBook
Download Your Free IoT in Healthcare Use Cases eBook
Read More
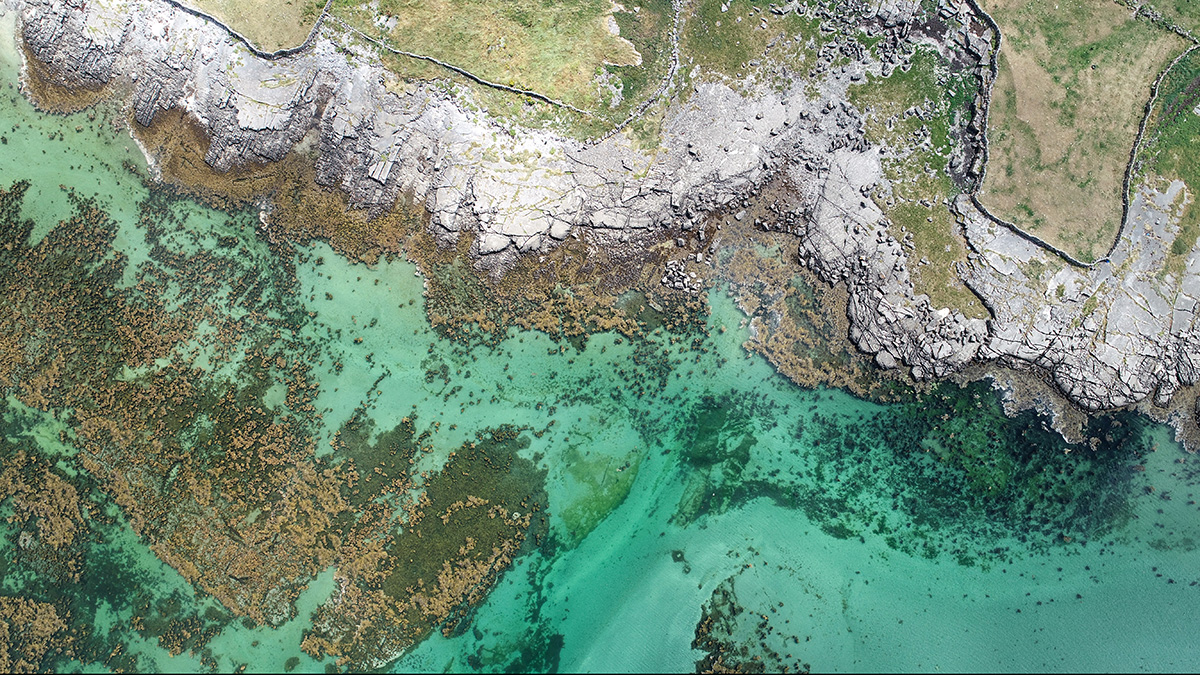


Nestled in the pristine environment of the Aran Islands, locals perform the ancient practice of hand-harvesting seaweed. The practice has remained relatively unchanged for hundreds of years. Used for centuries as both food and medicine, seaweed is in bountiful supply on the rugged Atlantic coastline. Amidst this wild and wonderful setting, Davra and Intel embarked on a fascinating use case for the Internet of Things (IoT).
In 2022, with the support of Intel, Davra embarked on a project with Aran Islands Seaweed (www.blathnamara.ie). The project aimed to use IoT and Intel technology to enhance the seaweed harvesting process.
The Aran Islands is certainly a unique and beautiful setting for IoT. The use cases, however, are familiar: condition monitoring, automation, computer vision, and asset tracking. Underpinning the whole project was a desire to build a sustainable and environmentally friendly business.
Aran Islands Seaweed is situated on Inishmore, the largest of the Aran Islands, off the coast of Galway. Their mission is to bring seaweed from tide to table. They achieve this using a specialised drying process that helps preserve the seaweed’s nutrients.
With 7,000 km of coastline and located in the warm waters of the Gulf Stream, Ireland has an abundance of seaweed. As such, seaweed harvesting has a long tradition in the region.
The contemporary uses of seaweed are numerous. People around the world use it as food, fertiliser, and incorporate it into various cosmetics and spa treatments. It is also the subject of research for its medicinal qualities.
Seaweed harvesting starts, of course, at the shoreline, where skilled harvesters carefully select and gather the seaweed by hand. The process is meticulous but necessary to preserve the fragile marine ecosystem. Harvesters only take mature seaweed, letting younger plants grow and maintaining the natural balance of coastal waters.
Harvesters then gently gather and transport the seaweed from the shoreline to the Aran Islands Seaweed processing facility. The seaweed then undergoes a delicate drying process using state-of-the-art dehumidifiers. This method maintains the seaweed’s natural properties while using much less energy than conventional drying methods.
The team then carefully mills the dried seaweed into a fine powder rich in nutrients and minerals. This powder finds its way into a variety of products, ranging from health foods to luxurious cosmetics.
We were delighted to be asked by Aran Islands Seaweed to digitise their operations. Their goals were clear – use real-time data and automation to streamline processes and create efficiencies. Underpinning everything was the desire for more sustainable and renewable practices.
To do this, we took a detailed look at their facilities and processes to understand where IoT could help. We identified two key use cases for IoT: quality control in the drying process and shoreline monitoring.
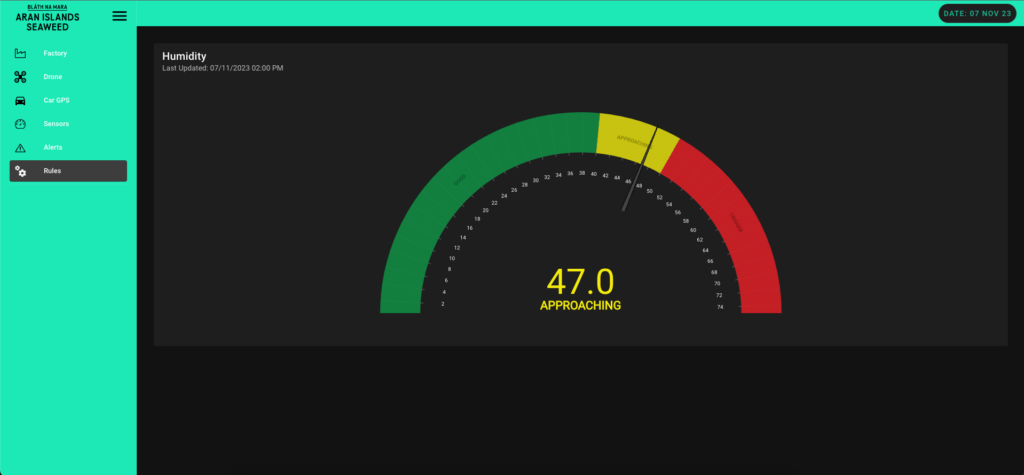
IoT sensors and connected devices monitor the humidity levels within the drying rooms. This real-time monitoring allows for immediate adjustments to maintain the ideal drying environment for the seaweed. This preserves its nutritional value and prevents degradation because of over or under-drying.
By precisely controlling the humidity, the drying process becomes more efficient. The IoT system’s ability to maintain optimal conditions reduces the need for prolonged drying times. This efficiency translates into lower energy consumption, as the drying equipment operates for shorter periods.
This, in turn, increases the facility’s throughput. Maintaining consistent humidity levels speeds up the drying process without compromising the seaweed quality.
The system can automatically adjust the settings of the dehumidifiers based on the sensor data. This automation ensures a consistent drying process and frees up staff for other important tasks. The team can also analyse the collected data from the sensors to refine the drying process further. Insights from this data may lead to future improvements in energy usage and drying efficiency.
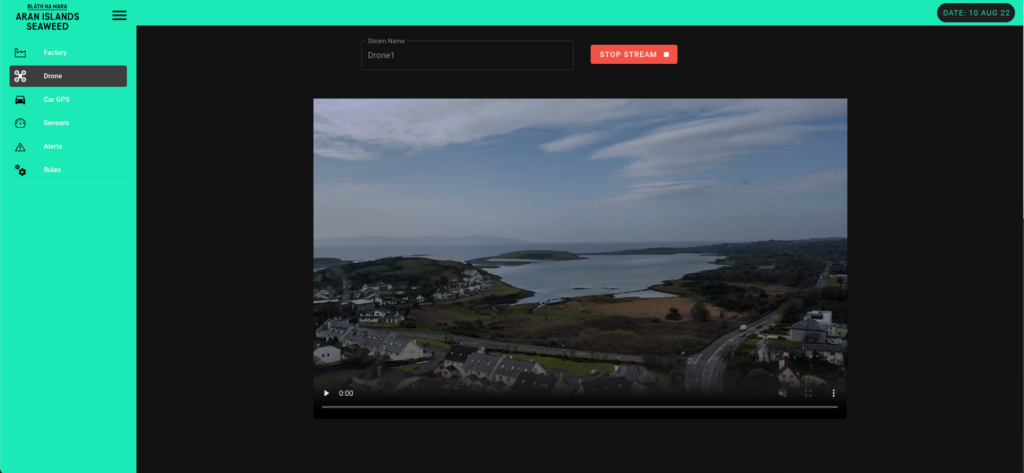
Utilising automated drones for foreshore monitoring offers a significant advantage in terms of overseeing seaweed growth and environmental conditions. These drones capture a wealth of useful data, providing insights that are crucial for sustainable seaweed harvesting.
Drones equipped with high-resolution cameras provide detailed aerial images of the foreshore. These images offer a comprehensive view of the seaweed beds, allowing for accurate assessments of seaweed density and distribution. The team then knows when the seaweed is at its peak nutritional value and the optimal time for harvesting.
Drones can capture indicators of environmental health, such as the presence of pollutants or changes in water quality. Footage combined with computer vision reveals any changes in the coastline and potential erosion, which might impact seaweed growth areas. Early detection of such changes allows for proactive measures to protect the foreshore.
Post-storm drone surveys can assess the impact of severe weather on seaweed beds. This is crucial for understanding and mitigating the effects of climate change on seaweed cultivation. Combining this data with other IoT data sources, such as weather stations, provides a comprehensive overview.
We also identified several secondary use cases that aligned with the goals of efficiency, sustainability, and environmental responsibility.
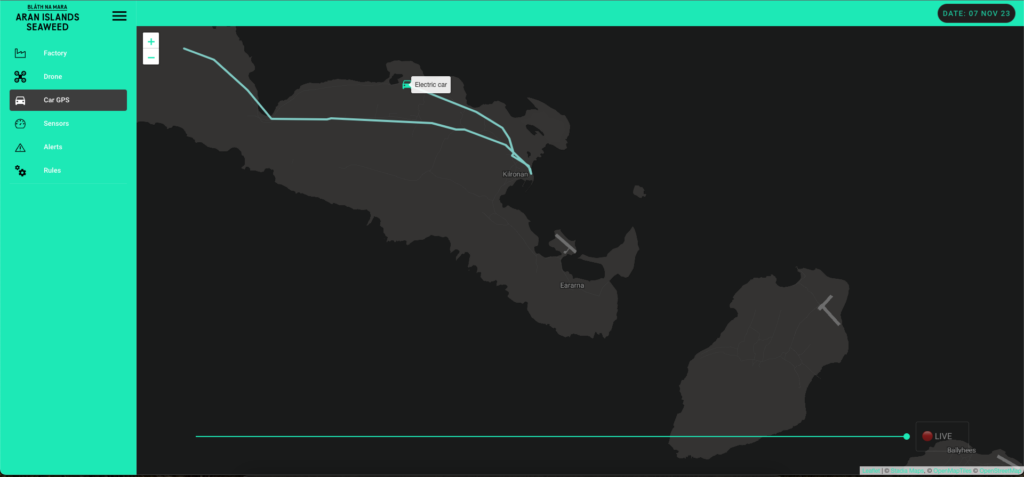
We equipped the facility’s EVs with IoT devices to monitor energy usage patterns. This helps in optimising routes and schedules for transportation needs, reducing the carbon footprint.
IoT sensors on factory equipment like hammer mills detect anomalies during operation. We can schedule predictive maintenance based on this data to prevent downtime and prolong equipment life.

IoT systems monitor the facility’s total power usage and pinpoint areas with potential energy efficiency enhancements. This aligns with the facility’s dedication to environmental stewardship.
Consequently, there have been notable improvements in energy management and equipment maintenance, reducing the environmental footprint and improving reliability.
IoT-enabled weather stations provide real-time data on local weather conditions. This data informs the team about the best times to harvest. Simultaneously, IoT helps to optimise the harvesting process while protecting the marine ecosystem.
The integration of IoT technology into the seaweed processing operations on the Aran Islands is a significant leap forward. IoT has helped Aran Islands Seaweed move the needle on its business and environmental goals. From global equipment manufacturers to seaweed farms, IoT offers value to all types of businesses.
Looking ahead, there is potential for further IoT expansions. Possibilities include more sophisticated data analytics for predictive maintenance, enhanced environmental monitoring systems, and even greater automation in seaweed processing. These improvements may result in greater yields, lower costs, and a more sustainable business overall.
Aran Islands Seaweed is a shining example of how traditional industries can embrace modern technology to improve their practices. Embracing IoT has improved the facility’s operations and set a benchmark for sustainable and efficient practices in the industry.
Download Your Free IoT in Healthcare Use Cases eBook

Davra IoT is the only Industrial IoT Platform Available on AWS Marketplace
Read MoreThe Collaboration of Humans & Robots Has Created The Cobot
Read More